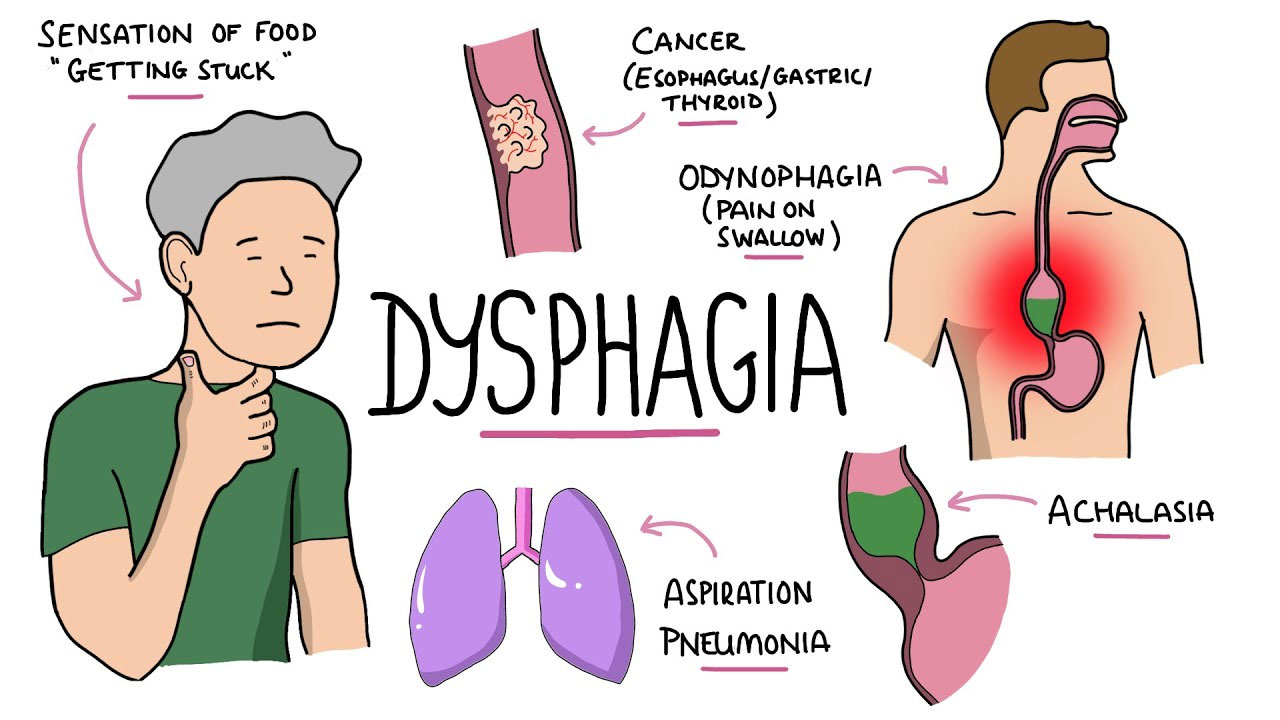
Dysphagia, a condition characterized by difficulty swallowing, can arise from various underlying health conditions. It isn’t a standalone disorder, but rather a symptom or consequence of other medical issues. This article will examine several common health conditions that can lead to dysphagia.
1. Stroke
Strokes are a leading cause of dysphagia. When a stroke occurs, it can damage the areas of the brain responsible for coordinating swallowing muscles and reflexes. This damage can result in difficulty in swallowing, which can range from mild to severe.
2. Neurological Disorders
Various neurological conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease and ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis), can affect the nerves and muscles involved in swallowing. These conditions can lead to dysphagia as a result of muscle weakness or impaired coordination.
3. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD):
GERD (a chronic condition) is characterized by the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus. Over time, this acid exposure can affect the esophagus, leading to inflammation or scarring that can cause dysphagia.
4. Esophageal Strictures
Esophageal strictures are narrowing of the esophagus, often due to scar tissue formation. Conditions like chronic acid reflux, radiation therapy, or the ingestion of caustic substances can lead to the development of strictures, making it difficult for food and liquids to pass through.
5. Head and Neck Cancer
Cancers of the head and neck region, including the throat, esophagus, or mouth, can result in dysphagia. Tumors in these areas can obstruct the passage of food and cause pain during swallowing.
6. Gastrointestinal Disorders
Certain gastrointestinal disorders, such as eosinophilic esophagitis or achalasia, can lead to dysphagia. Eosinophilic esophagitis is characterized by inflammation in the esophagus, while achalasia involves the malfunction of the lower esophageal sphincter, causing difficulty in the passage of food.
7. Age-Related Changes
As individuals age, they may experience age-related changes in the muscles and structures involved in swallowing. This can result in a condition known as presbyphagia, which is a normal age-related decline in swallowing function; a common solution is to add thickeners like Simply Thick thickening agent.
8. Medication-Induced Dysphagia
Certain medications, especially those that can dry out the mouth, may contribute to swallowing difficulties. Medications that affect the muscles or nervous system can also lead to dysphagia as a side effect.
9. Post-Surgical Complications
Surgeries involving the head, neck, or chest areas can lead to postoperative dysphagia, often due to tissue swelling, scarring, or nerve damage during the procedure.
10. Systemic Diseases
Some systemic diseases, such as lupus or sarcoidosis, can have a wide range of effects on the body, including the potential to cause dysphagia if they involve the esophagus or surrounding structures.
It’s essential to note that dysphagia can vary in severity and presentation depending on the underlying condition. Symptoms may include difficulty swallowing, pain while swallowing, choking, coughing, or regurgitation of food or liquids. If you or a loved one experiences persistent or worsening swallowing difficulties, it’s crucial to seek a prompt medical evaluation and diagnosis.
The management of dysphagia typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, including input from speech therapists, dietitians, and healthcare providers. Treatment options may include dietary modifications, swallowing exercises, medications, or, in some cases, surgical interventions to address the underlying cause.
In conclusion, dysphagia can be a challenging symptom that arises from various medical conditions, ranging from neurological disorders to gastrointestinal issues. Recognizing the conditions that might result in dysphagia is the first step toward early diagnosis and effective management. Seeking prompt medical evaluation and a tailored treatment plan is essential to improve the quality of life for individuals living with dysphagia.