Press Release (ePRNews.com) - BIDDEFORD, Maine - Feb 19, 2017 (UTC) - Human tissue is a complex combination of structural elements. Each structural element contributes in some way to the natural healing process, or cascade. Surgical sealants, glues and hemostatic products can be used to enhance, support and strengthen these natural processes. In addition, surgical procedures often involve the use of glues and sealants to repair internal tissues.
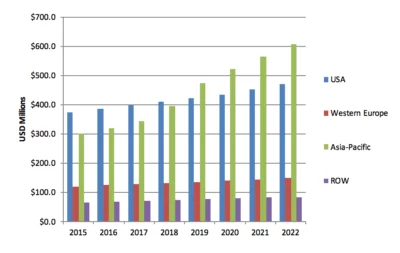
Medical and surgical glues, hemostats, and sealants constitute a $5.7 billion global market that is well developed, with hemostats growing fastest among all segments, and with sales in Asia/Pacific representing the highest regional growth. The global market will reach $9.3 billion by 2022, according to the leading source on these markets, MedMarket Diligence.
“As the market for sealants, glues and hemostats matures, sales are arising more from emerging markets than significant new products or applications,” says Patrick Driscoll of MedMarket Diligence. However, he reports that innovators have not run out of ideas and technologies to allow these products to push further and deeper into medical and surgical practice, making them easier to use in more complex procedures, alone or adjunctively, and further penetrating routine caseload.
Surgical sealants are most often used to stop widespread, oozy internal bleeding. The product may be sprayed on a bleeding surface, or applied internally using a patch. Sealants are considered inappropriate for heavy bleeding. Surgical sealants may be made of glutaraldehyde and bovine serum albumin, polyethylene glycol polymers, and cyanoacrylates. Fibrin sealants are made of a combination of thrombin and fibrinogen. Sealants may also be made from a patient’s blood (autologous).
Although the terms ‘glues’ and ‘adhesives’ are frequently used interchangeably, they are not the same. Medical glues as defined here are products used to make two tissue surfaces adhere securely to each other without coming apart under normal physical stress. The definition of medical glues does not include medical adhesives such as those coating a bandage to make it stick to the skin.
A hemostat is commonly used in both surgery and emergency medicine to control bleeding, such as from a torn blood vessel. Active hemostats contain thrombin products which may be derived from several sources, such as bovine pooled plasma purification, human pooled plasma purification, or through human recombinant manufacturing processes. Flowable-type hemostats are made of a granular bovine or porcine gelatin that is combined with saline or reconstituted thrombin, forming a putty that may be applied to the bleeding area. Mechanical hemostats, which generally require pressure to stop the bleeding, include items such as hemostatic clamps, absorbable gelatin sponge, collagen, cellulose, or polysaccharide-based hemostats applied as sponges, fleeces, bandages, or microspheres, and do not contain thrombin or any other active biologic compounds. Mechanical hemostats are not included in this report.
North America is the largest regional segment of the market, and the US market is by far the largest market in this region. The large US share can be attributed to several factors, including the continuing growth in the volume of surgeries, widening applications for surgical sealants and adhesives, an increasing number of FDA market approvals, extensive R&D activities, increasing attention from academic and government research on medical device development, and the presence of a large number of market players.
MedMarket Diligence has published, “Worldwide Markets for Medical and Surgical Sealants, Glues, and Hemostats, 2015-2022: Established and Emerging Products, Technologies and Markets in the Americas, Europe, Asia/Pacific and Rest of World.” (http://mediligence.com/s290/). This analysis of the global market, which the company has tracked for over 15 years, details the status of new product development and market introduction for these advanced products in wound management.
The report is described in detail, with table of contents and list of exhibits, at http://mediligence.com/s290/. The report and highlights of its findings have also been routinely covered in MedMarket Diligence’s “advanced medical technologies” blog (http://blog.mediligence.com).
Source : MedMarket DiligenceMedMarket Diligence, LLC
California United States
Phone: 949.859.3401
Website: http://www.mediligence.com





