The differences between data loggers and data acquisition systems (DAQ) have blurred over time, with the main distinctions of high speed vs low speed or high resolution vs low resolution largely disappeared.
Both acquire data for the purpose of computer analysis enabling companies to monitor the performance of machinery and staff for maintenance and improvement. Data is also used for analysis of accidents or incidents. Additionally, both can be acquired from high-quality distributors such as RS Components.
Data Loggers work from the ground up
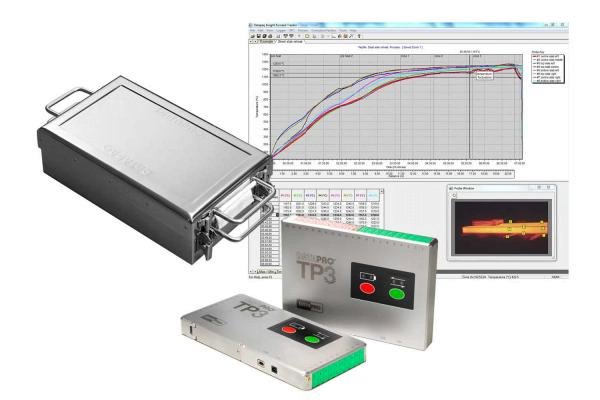
Data loggers are electronic devices that automatically monitor and record environmental parameters from a fixed location over a specific period of time. Increasingly based on a digital processor, a data logger is small, independently powered, portable, and incorporates a microprocessor, memory storage, and sensors.
The sensors measure a range of conditions including temperature, humidity, power usage, and other relevant parameters. All information is either stored in a memory card and collected for analysis manually, or is transferred via the internet.
Data loggers can use just one input channel or reach up to 100 depending on the limitations of the power source. Applications of data logging include weather station recording, hydrographic monitoring, soil moisture level recording or gas pressure vessel monitoring.
Specific devices such as temperature loggers can be used to collect data in locations that are sensitive to heat and cold for example warehouses, providing high level quality control.
Data loggers automatically collect data on a 24-hour basis unattended to measure and record information for the duration of the monitoring period. This provides a comprehensive, accurate and real-time picture of the environmental conditions being monitored.
Required to operate in harsh environmental conditions where computers will not function reliably, dataloggers are designed to be impervious to problems that might affect a general-purpose computer such as program crashes and operating system instability.
As well as being able to operate independently, data loggers are characterized by the following features:
Removable memory devices like SD memory cards
Usually slower sampling rates than data acquisition systems
Battery or solar powered.
Data Acquisition Systems take a birds-eye view
Data acquisition is a broader sampling of the real world and uses computer based software programmes to record data from multiple analogue and digital inputs.
DAQ involves acquisition of signals and analogue waveforms converting them into digital values for processing. The components of data acquisition systems translate measurements to an electrical signal which is displayed, analysed, and stored on a computer as digital numeric values that can be manipulated by the computer. Large-scale DAQ systems are used in laboratories or test cells with rack-based Input/Output and can reach upwards of 1,500 channels.
Software programmes to control the data acquisition system applications can be developed using various general purpose programming languages or are available as open-source software packages
In contrast to a Data Logger the DAQ characteristics are generally described as:
Faster sampling speeds
Run by software that delivers PC-based storage
Real time display of data.
The Data Logger and DAQ are both valuable tools in the condition monitoring process, performing a different yet equally important function.