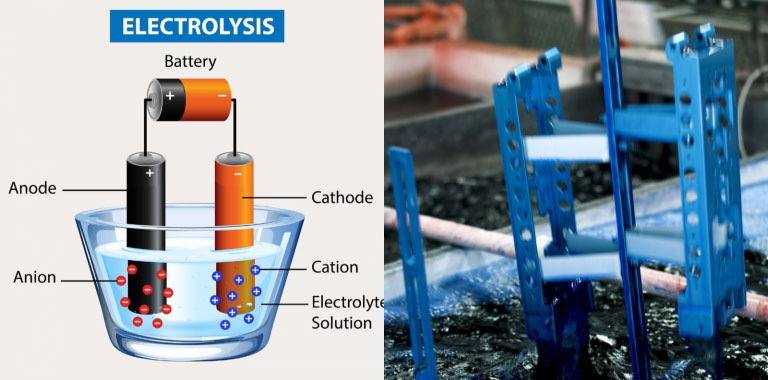
Anodizing is a decorative process that can be used on various metals to create a protective, lustrous coating. It’s also an electrochemical process in which the metal reacts with hydrogen and oxygen at high-potential electrodes. Anodization is commonly used to provide corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and aesthetic appeal to various metals.
Today, it’s almost universal for all new steel and aluminum products. This article covers everything you need to know about anodizing and how it is done.
What is anodizing?
Anodizing is a method of electrochemically coating metal parts with a protective oxide layer. The process is also known as electrochemical dipping (ECID), electrolytic anodizing, or potting. It’s a result of “electroplating,” a technique in which an electric current is used to deposit a layer of metal on the surface of an object. However, anodizing is not the same as electrolysis.
Electroplating is used to create a thin layer of metal on the surface of objects that are immersed in an electrolyte. Electrolytic anodizing occurs at different potentials and is used to create a protective coating. Anodizing is often used to provide corrosion and wear resistance to metal surfaces. It’s also popular for decorating commercial and industrial equipment, such as water and wastewater treatment plants. This type of coating is also used to create specialized or custom-branded hardware for businesses.
Flat stock, like the products offered here (https://fastmetals.com/pages/flat-stock), comes in several thicknesses and widths and can be made from various metals, including aluminum, brass, bronze, copper, and steel. It is used for everything from creating electrical connection points to forming decorative trim.
Steps in the Anodizing Process
Electrolysis – This is a process where a solution is used to create a current that causes the metal to be deposited on the object’s surface. The process is done at a high potential, typically between 2.2 and 3.8 volts, and is often done using an electroplating tank. The tank is filled with an electrolyte solution, a salt solution that conducts electricity and is usually made up of sodium chloride or potassium hydroxide.
The metal part is submerged in the electrolyte, which causes the current to flow through it and deposit a metal layer on the object’s surface. The process takes place at a controlled rate, changing the electrolyte frequently to ensure even deposit distribution. Electrolysis is commonly used for anodizing aluminum but can also be used for anodizing stainless steel and other types of metal.
Electroplating is the same process as electrolysis, but in an electrolyte made up of acid. The metal part is submerged in the acid solution, which deposits a metal layer on the object’s surface.
Electroplating is often used for anodizing copper and for anodizing aluminum, stainless steel, and other metals. The acid used in electroplating can be an inorganic acid such as sulfuric acid or an organic acid like acetic acid. Acid can be used to remove impurities and solidify the deposit. The process is also used for gold anodizing, which is a multi-step process that’s not used for anodizing other types of metal.
Advantage of Anodizing
- Corrosion Resistance
- Wear Resistance
- Scratch Resistance
- Good Looks
- Customization
- Low Cost – Environmental Benefits
Disadvantage of Anodizing
- Long Production Times
- Safety Concerns
- Limited Color Choices
- Limited Design Options
- Higher Energy Costs
- Complex Equipment Maintenance
- Complex Processes
Conclusion
Anodizing is an electrochemical process usually done for the protection of various metals. It saves metal from rust and keeps it shining for years.