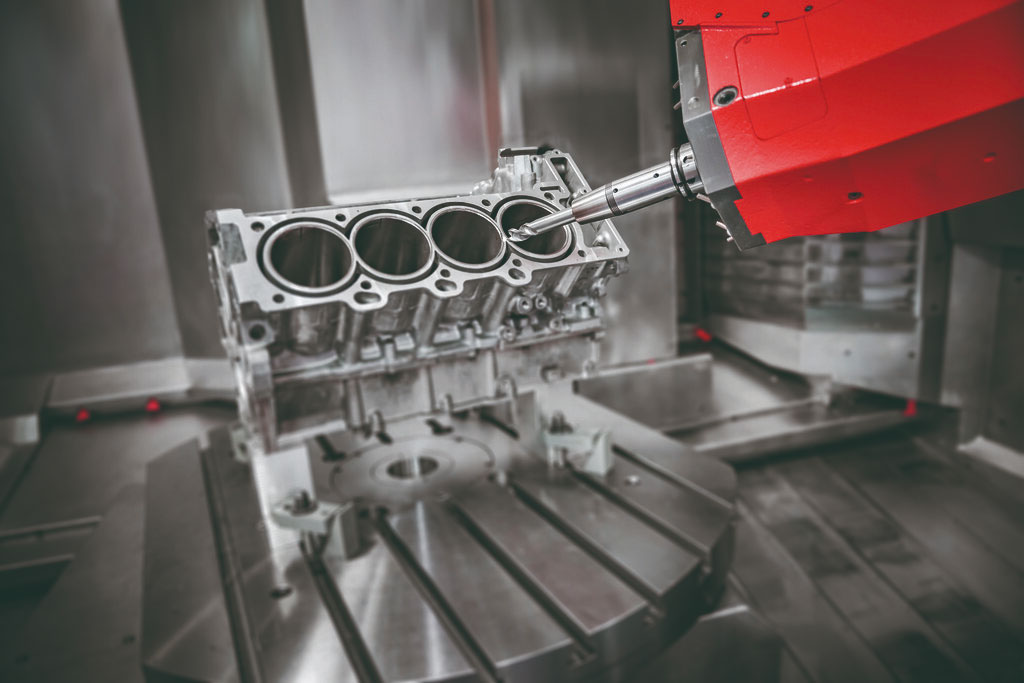
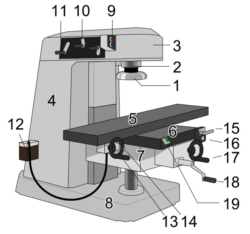
Delving into the world of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) milling can be a thrilling experience for enthusiasts and professionals alike. The precise manufacturing technique that revolutionizes industries by creating complex, custom-made parts is nothing short of fascinating. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the ins and outs of CNC milling, including its advantages and applications in various sectors.
What is CNC Milling?
CNC milling is an advanced manufacturing process that involves the use of a computer to control the movement of cutting tools across a workpiece. The process is designed to remove material from the workpiece, resulting in the creation of intricate, three-dimensional parts with high precision and accuracy. It’s an essential technique used in industries ranging from aerospace to automotive, electronics to medical, and beyond.
How Does CNC Milling Work?

CNC Milling Machines
At the heart of the CNC milling process is a sophisticated machine equipped with a variety of cutting tools and mechanisms. These machines come in various forms, including vertical and horizontal configurations, with multi-axis capabilities to achieve the desired level of precision and intricacy. The essential components of a CNC milling machine include a spindle, cutting tools, workpiece holding devices, and a computer control unit.
The Milling Process
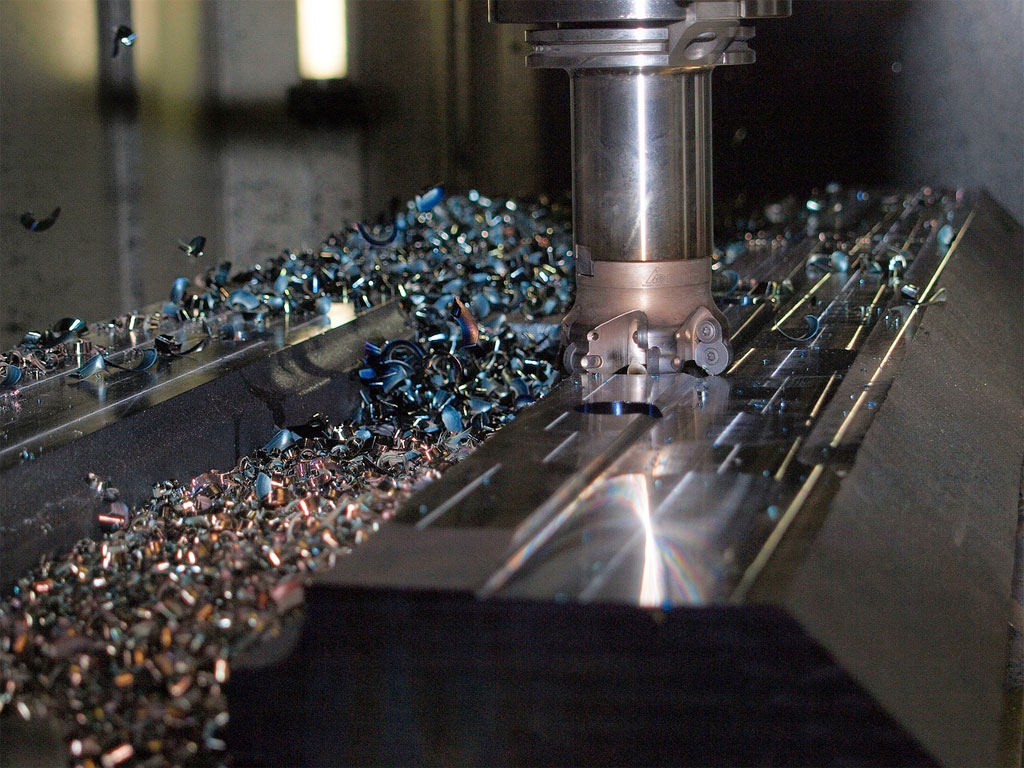
The CNC milling process begins with a computer-aided design (CAD) model of the desired part. This digital blueprint is then converted into a set of machine-readable instructions known as G-code. Once the G-code is loaded into the CNC milling machine, the computer control unit interprets the code and directs the cutting tools to move along specific paths to remove material from the workpiece. The milling process can involve various cutting techniques, such as face milling, peripheral milling, and contour milling, depending on the desired part geometry and surface finish.
Advantages of CNC Milling
CNC milling offers a myriad of benefits, making it a popular choice for various industries. Some of the most notable advantages include:
High precision and accuracy: CNC milling machines follow precise instructions from computer-generated G-code, resulting in the production of parts with tight tolerances and exceptional quality.
Complex geometries: The multi-axis capabilities of CNC milling machines allow for the creation of intricate, three-dimensional parts that would be difficult or impossible to achieve through manual methods.
Rapid prototyping: CNC milling enables quick and efficient production of prototypes, helping businesses shorten their product development cycles and bring new products to market faster.
Reduced labor costs: The automated nature of CNC milling eliminates the need for manual intervention, resulting in lower labor costs and increased productivity.
Scalability: CNC milling machines can produce both small and large quantities of parts, making it a flexible and cost-effective solution for various production needs.
Applications of CNC Milling
CNC milling has found its way into a diverse range of industries, each with unique requirements and applications. Some prominent sectors that benefit from CNC milling include:
Aerospace: The production of complex, high-precision components for aircraft and spacecraft, such as engine parts, landing gear, and structural components.
Automotive: CNC milling is used to create intricate parts for engines, transmissions, suspension systems, and more, ensuring optimal performance and durability.
Electronics: The process is employed to manufacture circuit boards, housings, and other components for electronic devices, including smartphones, laptops, and wearables.
Medical: CNC milling plays a critical role in the fabrication of surgical instruments, implants, and prosthetics, ensuring the highest level of precision and reliability.
Moldmaking: The technique is utilized in the production of molds and dies for injection molding and other manufacturing processes, ensuring accurate and repeatable results.
Energy: CNC milling is involved in the production of components for renewable energy systems, such as wind turbines and solar panels, promoting a sustainable future.
Jewelry: The process allows for the creation of intricate and unique jewelry designs, showcasing exceptional craftsmanship and attention to detail.
Materials Used in CNC Milling
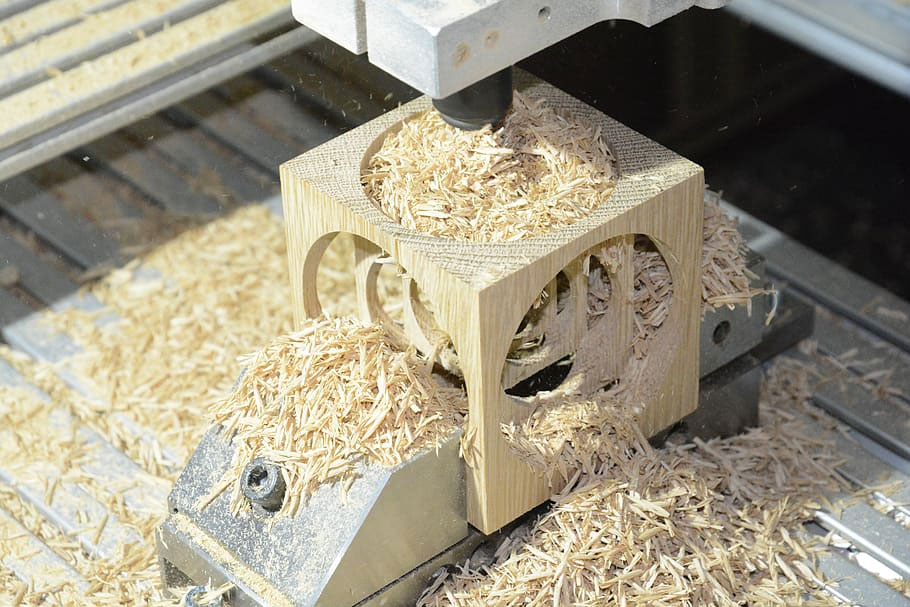

A wide range of materials can be processed using CNC milling machines, catering to the diverse needs of various industries. Some commonly used materials include:
Metals: Aluminum, steel, brass, bronze, and titanium are frequently milled to produce durable and robust components.
Plastics: High-performance plastics like ABS, nylon, polycarbonate, and PEEK are milled for lightweight and corrosion-resistant parts.
Wood: CNC milling can shape different types of wood, including hardwood, softwood, and engineered wood, for various applications such as furniture, cabinetry, and art pieces.
Composites: Advanced composite materials, such as carbon fiber and fiberglass, can be milled for high-strength, lightweight components.
CNC Milling Software and Tooling
The success of CNC milling relies heavily on the software and tooling used in the process. Here are some essential aspects to consider:
CAD/CAM Software
Computer-aided design (CAD) software is used to create digital models of the parts to be milled. These models are then converted into machine-readable G-code using computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software. Several CAD/CAM software options are available, each with its own set of features and capabilities.
Cutting Tools
CNC milling machines employ a variety of cutting tools to achieve the desired part geometry and surface finish. These tools can be broadly classified into end mills, face mills, and specialty mills, with various subtypes such as ball nose, corner radius, and chamfer mills. The choice of cutting tool depends on the material being milled, the desired part geometry, and the required surface finish.
Workholding Devices
Workholding devices are essential for securing the workpiece during the milling process. Common workholding solutions include vises, clamps, and vacuum chucks. The choice of workholding device depends on the size, shape, and material of the workpiece, as well as the milling operations to be performed.
Conclusion
CNC milling is a versatile and efficient manufacturing process, capable of producing complex, high-precision parts for a wide range of industries. By harnessing the power of computer-controlled machinery and sophisticated cutting tools, CNC milling has revolutionized the way we manufacture and design products. From rapid prototyping to large-scale production, CNC milling continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible in the world of manufacturing, paving the way for new innovations and breakthroughs.